इस पोस्ट मे हम 10 वी कक्षा के 8 वी अध्याय “समझें धातु अधातु” के प्रश्नोत्तर करेंगे. नीचे दिए वीडियोस से आप सीख सकते हैं. प्रश्नों को एक बार खुद से सुलझाने के बाद नीचे उसके उत्तर देख सकते हैं.
In this post, QnAs of 8th chapter Metals and Non metals is covered. Please make best use of the references provided to learn and attempt answering the questions by yourself first. Answers follows the list of questions. All the best!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=syQwvZWahxI Part -1
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fPWHsje3Qxo Part -2
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TrC9Px06RhI Part – 3
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XAu4RQ6uCTg Part -4
( Reference for Aluminium Extraction: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WaSwimvCGA8 )
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
स्वाध्याय 10-वी कक्षा Self-learn 10th standard
विभाग-ब अध्याय–८ समझे धातु-अधातु Section-B Chapter 8 Understanding Metals and Non-metals
प्रश्न Questions
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
प्र. १ नाम लिखें (Write the names of following)
१) उभयधर्मी ऑक्साइड तैयार करनेवाला धातु : _____________ 1) Amphoteric oxide forming metal:______________
२) तांबे तथा जस्ते का सम्मिश्रण : ________________ 2) Alloy of Copper and Zinc: __________________
३) अल्यूमिनियम निष्कर्षण मे विधयुत अपघटन विलयन मे तापमान कम करने उपयोग मे आनेवाला यौगिक : __________
3) Compound used in electrolytic extraction of Aluminium for reducing melting point of mixture: _____________
४) ठंडे पानी से अभिक्रिया न करनेवाला धातु परंतु बाश्प से अभिक्रिया करने वाला एक धातु : ________________
4) One metal that doesn’t react with cold water but reacts with hot water vapour: __________________
५) अल्यूमिनियम के सामान्य आयस्क (Ore): __________ 5) Common ore of Aluminium: _________________
प्र.२ नीचे दिए गये विशेषताओं के आधार पर आधातु तथा उनके यौगिकों को लाघु होने वाली पाँच विशेषताएँ कौनसी है लिखिए.
Find the 5 properties associated with non-metals and their compounds
१) तन्यता (Ductility)
२) विद्युत का बहन (Electrical Conductivity)
३) अम्लीय ऑक्साइड (Acidic Oxide)
४) एनोड पर मुक्त होनेवाला (Liberates in Anode)
५) क्षारीय ऑक्साइड (Alkaline oxide)
६) भंगूर (Brittle)
७) (१, २, ३) संयोजकता एलेक्ट्रान ( 1,2 or 3 valence electrons)
८) कॅतोड पर मुक्त होने वाला (Liberates in Cathode)
९) (५, ६, ७) संयोजकता एलेक्ट्रान ( 5,6 or 7 valence electrons)
प्र ३) निम्न रूप मे पाए जानेवाले धातुओं के नाम लिखो (Write names of metals found in the following form)
१) सल्फायड (Sulfide)
२) कार्नबनेट (Carbonate)
३) ऑक्साइड (Oxide)
प्र ४) निम्न को स्पष्ट करो (Define the following)
१) खनीज (Mineral): __________________________________________
२) मृदाअशुध्धि (Gangue): _______________________________________
३) अयस्क (Ore): _____________________________________________
४) धातुविज्ञान (Materials Science): _________________________________
५) भंजन (Roasting): __________________________________________
प्र ५) वैज्ञानिक कारण लिखो (Give scientific reason)
१) सोडियम को हमेशा मिट्टी के तेल मे रखते हैं. Sodium is kept in kerosene oil.
२) सोना तथा चाँदी का उपयोग गहने बनाने के लिए करते हैं. Gold and silver is used for making jewellery.
३) पानी से क्रिया होनेपर कॅल्षियम पानी मे तैरता है. Calcium floats on water when it reacts.
४) आयनिक यौगिकों का द्रावणांक तथा क्वतांक उच्च होता है. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
५) काले पड़े हुए तांबे के बर्तन सॉफ करने के लिए नींबू या ईमली का उप्यूग होता है. Blackened copper utensils are cleaned by lemon or tamarind.
प्र ६) सुधाने तांबे का सिक्का सिल्वर नाइट्रेट के विलयन मे डुबया. थोड़े समय पश्चात उसे वह सिक्का चमकता हुआ दिखा.
क्यों ? संतुलित रसायनिक समीकरण लिखो.
Rusted copper coin is put in silver nitrate solution. After sometime it started to shine. Write balanced equation.
प्र ७)‘A’धातु का एलेक्ट्रॉनिक समीकरण 2,8,1 है. ‘B’ धातु का एलेक्ट्रॉनिक समीकरण 2,8,8,2 है. कौनसी धातु अधिक क्रियाशील है ? उसे पहचानो. उसकी तनु हाइडरोक्लॉरिक अम्ल के साथ होने वाली अभिक्रिया लिखो.
‘A’ metal has electronic configuration 2,8,1. ‘B’ metal has electronic configuration 2,8,8,2. Which is more reactive? Write its reaction with dilute hydrochloric acid.
प्र ८) जस्ते के सल्फ़ाईड से जस्ता प्राप्त करने दो रसायनिक अभिक्रिया होती है.
Extraction of Zinc from Sulfide involves 2 chemical reactions.
ZnS (भंजन/Roasting) —>
ZnO (अवकरण/Reduction) —->
A तथा B के लिए समीकरण लिखो. Give the products of the reactions
प्र ९) निम्न विधानों के रसायनिक समीकरण मे रूपांतरण करके उसे संतुलित करो.
Give chemical reactions which occur under following conditions.
१) अल्यूमिनियम पर से बाश्प प्रवाहित की गई. Water vapour is passed over Aluminium.
२) तांबे का उसके सल्फायड धातु से निष्कर्षण.Extraction of copper from its sulphide.
३) उष्मा के प्रभाव (Thermit) अभिक्रिया.Thermit reaction.
४) अल्यूमिनियम ऑक्साइड, जलीय सोडियम हाइडरॉक्साइड के विलयन मे घुलने से क्या होगा ?
What happens when aluminium oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide.
प्र १०) अल्यूमिनियम के निष्कर्षण मे In Aluminium purification
१) बॉक्साइट का सांदीकरण करने के पद्धति का नाम लिखो. Write the name of the method for purification of bauxite.
२) अल्यूमिनियम का विद्युत अपघटनी क्षरण होते समय कॅतोड पर होने वाली अभिक्रिया लिखो.
On electrolytic reduction of aluminium, write the reaction that happens in cathode.
३) क्रायॉलैइट के कार्य तथा सूत्र लिखो. Write the formula and function of cryolite
४) अल्यूमिनियम हाइडरॉक्साइड पर उष्मा के प्रभाव का संतुलित रसायनिक समीकरण लिखिए.
Write balanced equation for the effect of heat on aluminium hydroxide.
५) अल्यूमिनियम निष्कर्षण की नामांकित आकृति बनाओ. Draw diagram of aluminium extraction.
६) समय समय पर एनोड बदलना क्यों आवश्यक है ? Why should anode be changed time to time ?
७) अल्यूमिनियम के यौगिक को सांद्र कॉस्टिक सोडे के साथ गर्म करने पर क्या होगा ? संतुलित रासायनिक समीकरण लिखो.
What happens when aluminium hydroxide is heated with concentrated caustic soda? Write balanced equation.
प्र ११) समिश्र मे जंग लगने सा रोकने की दो पद्धतियाँ लिखो. Describe two methods for preventing corrosion of alloys.
प्र १२) समिश्र अर्थर्थ क्या ? रसायनिक घटकों के साथ दो उदाहरण लिखो. What are alloys? Give 2 examples with chemical composition.
प्र १३) निम्न धातुओं को उनके अभिक्रीयाशीलता के उतरते क्रम मे लिखो. Write in decreasing order of metal reactivity
Cu, Mg, Fe, Na, Ca, Zn
प्र १४) धातु तथा आधातु मे एलेकट्रोनों का लेनदेन होकर आयनिक यौगिक कैसे बनते हैं, स्पष्ट करो. धातु Mg तथा Cl आधातु इनकी सहायता से उत्तर स्पष्ट करो.
Describe how metals and non metals react with exchange of electrons with the help of Mg and Cl as example.
प्र १५) ‘X’ तत्व की ऑक्सिजन से अभिक्रिया होकर X2O यह ऑक्साइड बनता है. यह ऑक्साइड पानी से घुलता है तथा इसमे लाल लिटमस नीला होता है. X तत्व धातु है या आधातु एक उदाहरण के साथ स्पष्ट करो.
‘X’ element forms X2O oxide with oxygen. When oxide dissolves in water, it changes red litmus blue. Is ‘X’ a metal or non-metal, explain with example.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
स्वाध्याय 10-वी कक्षा (महाराष्ट्रा शिक्षण-मंडल) Self-learn 10th standard (Maharashtra Board)
विभाग-ब अध्याय–८ समझे धातु-अधातु Section-B Chapter 8 Understanding Metals and Non-metals
उत्तर Answers
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
प्र. १ नाम लिखें (Write the names of following)
१) उभयधर्मी ऑक्साइड तैयार करनेवाला धातु : अल्यूमिनियम 1) Amphoteric oxide forming metal: Aluminium
२) तांबे तथा जस्ते का सम्मिश्रण : पीतल 2) Alloy of Copper and Zinc: Brass
३) अल्यूमिनियम निष्कर्षण मे विधयुत अपघटन विलयन मे तापमान कम करने उपयोग मे आनेवाला यौगिक: क्रयोलैइट
3) Compound used in electrolytic extraction of Aluminium for reducing melting point of mixture: Cryolyte
४) ठंडे पानी से अभिक्रिया न करनेवाला धातु परंतु बाश्प से अभिक्रिया करने वाला एक धातु : मॅग्नीज़ियम (Mg)
4) One metal that doesn’t react with cold water but reacts with hot water vapour: Magnesium (Mg)
५) अल्यूमिनियम के सामान्य आयस्क (Ore): बॉक्साइट 5) Common ore of Aluminium: Bauxite
प्र.२ नीचे दिए गये विशेषताओं के आधार पर अधातु तथा उनके यौगिकों को लाघु होने वाली पाँच विशेषताएँ कौनसी है लिखिए.
Find the 5 properties associated with non-metals and their compounds.
१) विद्युत का बहन (Electrical Conductivity): धात्विक गुण क्योंकि धातुओं के मुक्त एलेक्ट्रॉन्स का विद्युत बल मे बहना संभव है. Property of metal due to presence of free electrons which can move under electromotive force.
२) तन्यता (Ductility): धात्विक गुण क्योंकि धातुओं मे, अणुओं का उनके स्वतंत्र एलेकट्रोनों के बीच समानुवर्ती (हर दिशा से एक समान) धात्विक बंधन के वजह से, खींचाव बल लगने पर दरार बनने के बदले विस्थापन/सरकन हो जाता है.
Property of metal due to easy dislocation and movement of metal atoms in lattice bound by isotropic metallic bond amidst the sea of free electrons on application of tensile force, instead of cracking.
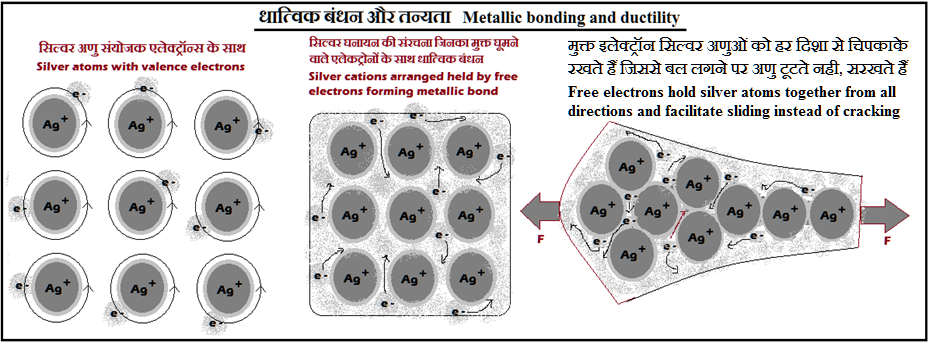
३) भंगूर (Brittle): अधातु गुण क्योंकि उनमे, संयोजक एलेक्ट्रॉन्स से अणु, घनिष्ठ एवं दिशात्मक सहसंयोजक बंधन मे होते है, और मुक्त एलेक्ट्रॉन्स नही होते जो बल लगने पर अणुओं मे परस्पर विस्थापन/सरकन को संभाल सकें, इसीलिए वे टूटते हैं.
Non-metallic property as in them, atoms are held by the valence electrons forming strong directional covalent bonds, and as there are no free electrons to support the displacement/sliding of atoms, they break when force is applied.
४) क्षारीय ऑक्साइड (Alkaline oxide): धात्विक गुण क्योंकि धातु पानी मे गलने पर एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को त्याग करते हैं और OH– बन जाता है.
Na2O + H2O –> 2 NaOH –> 2 Na+ + 2 OH–
Property of metal oxide as they dissolve in water and give away electrons so that OH– gets formed.
Na2O + H2O –> 2 NaOH –> 2 Na+ + 2 OH–
५) अम्लीय ऑक्साइड (Acidic Oxide): अधात्विक ऑक्साइड का गुण क्योंकि वे एल्कट्रोंस को संग्रह करके H+ छोड़ देते हैं.
CO2 + H2O –> H2CO3 –> 2H+ + CO32-
Property of non-metal oxide to as they try take electrons when dissolved in water and give away H+.
CO2 + H2O –> H2CO3 –> 2H+ + CO32-
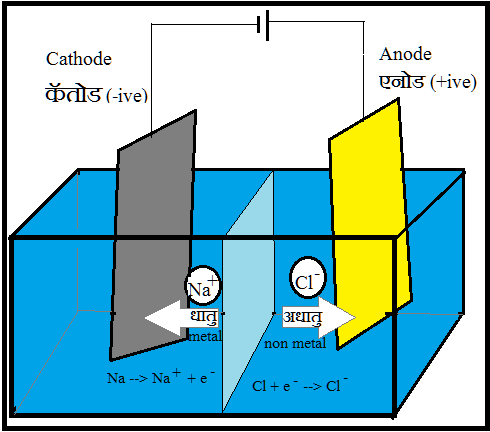
६) एनोड पर मुक्त होनेवाला (Liberates in Anode): अधातुओं का गुण क्योंकि वे विद्युत-अपघट्य विलयन मे ऋुनायन (-) के रूप मे होते हैं और
धनायन (+) एनोड की ओर आकर्षित होते हैं और उनका आक्सिकरण होता है.
2Na+ + 2Cl– –> 2Na (कॅतोड) + Cl2 (एनोड)
Property of non-metal as they are in the form of anions (-) in the electrolytic solution and migrate towards positively charged anode (+) to undergo oxidation. For eg: 2Na+ (aq)+ 2Cl– (aq) –> 2Na (Cathode) + Cl2 (Anode)
७) कॅतोड पर मुक्त होने वाला (Liberates in Cathode): धातुओं का गुण क्योंकि वे विद्युत-अपघट्य विलयन मे घनायन (+) के रूप मे होते हैं और ऋण (-) कॅतोड की ओर आकर्षित होते हैं और उनका न्यूनीकरण होता है.
2Na+ + 2Cl– –> 2Na (कॅतोड) + Cl2 (एनोड)
Property of metals as they form cations (+) in the electrolytic solution and thus migrate towards negatively charged cathode (-) to undergo reduction.
Eg. 2Na+ (aq)+ 2Cl– (aq) –> 2Na (Cathode) + Cl2 (Anode)
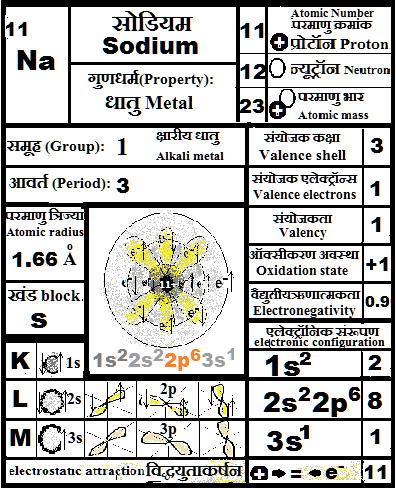
८) १, २, ३ संयोजक एलेक्ट्रान ( 1,2 or 3 valence electrons): धात्विक गुण जहाँ वे १, २, या ३ संयोजक एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को दे देते हैं.
उनकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था धनात्मक होती है. (+1, +2 & +3)
Property of metals as 1,2 and 3 valence electrons are easy to give away. Their oxidation state can be positive (+1, +2 and +3)
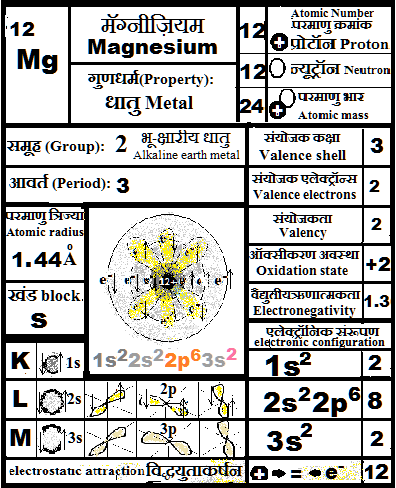
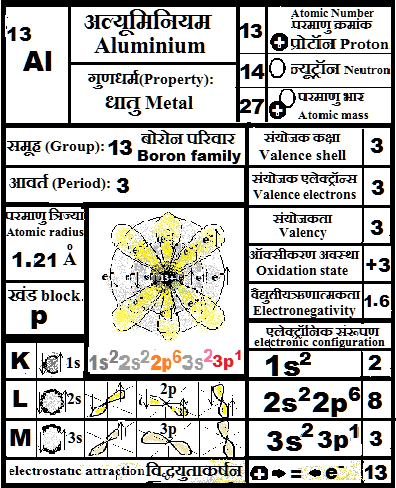
९) ५, ६, ७ संयोजक एलेक्ट्रान ( 5,6 or 7 valence electrons): अधात्विक गुण क्योंकि वे एलेक्ट्रान ग्रहण करके संयोजक कक्षा को पूर्ण (कुल 8 एलेक्ट्रॉन्स) करना चाहते हैं. उनकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था ऋणात्मक होती है. (-1, -2 & -3)
Property of non-metal as they try to gain electrons to have complete octet (8) in valence shell. Their oxidation state can be negative (-1, -2 & -3).
प्र ३) निम्न रूप मे पाए जानेवाले धातुओं के नाम लिखो (Write names of metals found in the following form)
उ १) सल्फायड (Sulfide): निकल Nickel (NiS) & तांबा Copper (CuS)
उ २) कार्नबनेट (Carbonate): कॅल्षियम Calcium (CaCO3) & मॅग्नीज़ियम Magnesium (MgCO3)
उ ३) ऑक्साइड (Oxide): अल्यूमिनियमAluminium (Al2O3) & लोहा Iron (Fe2O3)
प्र ४) निम्न को स्पष्ट करो (Define the following)
उ १) खनीज (Mineral): खनीज एक प्राकृतिक रूप मे पाए जाने वाली अकरबॉनिक, ख़ासकर धातुओं के ठोस यौगिक है या अनेक योगिकों का मिश्रण है जिनके निश्चित रसायनिक और परमाण्विक संरचना है.
A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic solid, especially containing metallic compounds or mixture of it in a definite chemical composition range, and an ordered atomic arrangement.
उ २) मृदाअशुध्धि (Gangue): अयस्क मे धातु यौगिक के साथ कुछ अशुद्धियाँ करीब रूप से जुड़ी हुई होती हैं. उन अशुद्धियों को मृदाअशुध्धि कहते हैं.
In an ore, some impurities are closely associated with the metal compounds. Those impurities are known as gangue.
उ ३) अयस्क (Ore): जिन खनीजों से धातुओं का निष्कर्षण आर्थिक रूप से लाभदायक हो सकता है उसे अयस्क कहते हैं.
Those minerals from which extraction of a metal or product is commercially profitable are known as ores.

(Source: http://www.rocksmineralscollections.com/metallic-ores.php )
उ ४) धातुविज्ञान (Materials Science): धातुविज्ञान विज्ञान का ही एक शाखा है जिसमे पधर्तों के संबंधी उनके शोधन, संश्लेषण, प्रसंस्करण, संरूपण, गुणधर्म और प्रदर्शन के खोज और परीक्षण होते हैं,जिनका कोई अभियांत्रिकी उपयोग होता है. जो गुण की हमे दिलचस्पी है वे मशीनी, विद्युत-चुंबकीय, प्रकाशीय आदि हो सकते है और उनका उपयोग एलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स, संचार, औषधि, यातायात, उत्पादन, निर्माण, मनोरंजन, उर्जा, या प्राकृतिक संरक्षण में हो सकता है.
Materials Science involves the study of the relationships between the synthesis, processing, structure, properties, and performance of materials that enable an engineering function. The properties of interest can be mechanical, electrical, magnetic or optical; the engineering function can impact industries involved in electronics, communications, medicine, transportation, manufacturing, recreation, energy, and the environment conservation.
( Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JZ9BkoLWdlg– Advanced Metallic Systems CDT)
उ ५) भंजन (Roasting): भंजन एक उष्ण प्रसारित गैस-ठोस अभिक्रिया है, जिनमे आक्सिकरण, अपघटन, क्लोरिनेशन, सलफेशन या उष्म-जलीय विश्लेषण हो सकता है. भंजन मे अयस्क का गर्म हवा के साथ अभिक्रिया होता है. ये सलफ़ैड अयस्कों पर किया जाता है जिससे वो ऑक्साइड मे परिवर्तन होते हैं और सलफर डाइयाक्साइड गैस निकलता है. तांबे और जसते के सलफ़ैड अयस्कों का भंजन होता है. उदाहरण ( Cu2S + O2 → 2 Cu + SO2 ) & ( 2 ZnS + 3 O2 → 2 ZnO + 2 SO2 )
Roasting consists of thermal gas–solid reactions, which can include oxidation, reduction, chlorination, sulfation and pyrohydrolysis. In roasting, the ore or ore concentrate is treated with very hot air. This process is generally applied to sulfide minerals. During roasting, the sulfide is converted to an oxide, and sulfur is released as sulfur dioxide, a gas. For the ores Cu2S (chalcocite) and ZnS (sphalerite), balanced equations for the roasting are:
( Cu2S + O2 → 2 Cu + SO2 ) & ( 2 ZnS + 3 O2 → 2 ZnO + 2 SO2 )
प्र ५) वैज्ञानिक कारण लिखो (Give scientific reason)
१) सोडियम को हमेशा मिट्टी के तेल मे रखते हैं. Sodium is kept in kerosene oil.
उ १) सोडियम हवे मे ऑक्सिजन के साथ सोडियम ऑक्साइड बन जाता है और अगर पानी लग जाए तो जोरों के साथ सोडियम हाइडरॉक्साइड बन जाता है. इसीलिए उसे केरोसिन मे रखते हैं.
Sodium reacts with oxygen in air to form sodium oxide. It can also react with water vigorously to form sodium hydroxide. To prevent its loss it is kept in kerosene to protect it from moisture and air.
२) सोना तथा चाँदी का उपयोग गहने बनाने के लिए करते हैं. Gold and silver is used for making jewellery.
उ २) सोना और चाँदी अत्याधिक अक्रियाशील धातु हैं जिनका सामान्य वातावरण मे रसायनिक अभिक्रिया जैसे आक्सिकरण या क्षरण नही होता, जिससे वे अपनी चमक नही खोते. उनकी तन्यता भी अच्छी है जिससे उनमे पेचीदे रूप-आकार दे सकते हैं.
Gold and silver are among least reactive metals, i.e. they do not react to get oxidized or rusted under normal conditions and does not lose its shine, and they also possess high ductility that helps make intricate designs.
३) पानी से क्रिया होनेपर कॅल्षियम पानी मे तैरता है. Calcium floats on water when it reacts.
उ ३) कॅल्षियम और पानी के अभिक्रिया से कॅल्षियम हाइडरॉक्साइड और हाइड्रोजन गैस बनते हैं. जब हाइड्रोजन गैस के बुलबुले ठोस कॅल्षियम के बीच फस जाते हैं, उनका कुल घनत्व कम होता है और वो पानी के उपर तैरता हैं.
Ca + 2H2O –> Ca(OH)2 + H2 (g)
Reaction between calcium and water yields calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. As the hydrogen gas gets trapped in the calcium matrix, their net density is low so it floats over water.
Ca + 2H2O –> Ca(OH)2 + H2 (g)
४) आयनिक यौगिकों का द्रावणांक तथा क्वथनांक उच्च होता है. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
उ ४) आयनिक यौगिकों मे धनायन और ऋणायन के बीच बलशील विद्युत आकर्षण होता है जिसे आयनिक बंधन कहते हैं. उन्हे तोड़ने के लिए उच्च ऊर्जा की ज़रूरत होती है, इसीलिए उनके द्रावणांक और क्वथनांक अधिक होता है.
Ionic compounds have very strong bonding between them due to electrostatic force of attraction between cation and anion. Thus high energy is needed to break the bonds, so they have high melting and boiling points.

( Source: http://vbteachingandlearning.blogspot.in/2015/11/types-of-solids.html )
५) काले पड़े हुए तांबे के बर्तन सॉफ करने के लिए नींबू या ईमली का उप्यूग होता है. Blackened copper utensils are cleaned by lemon or tamarind.
उ ५) तांबा वातावरण मे ऑक्सिजन के संपर्क से काले रंग का ऑक्साइड बनता है. नींबू मे सिटरिक अम्ल और ईमली मे टर्तरिक अम्ल होते हैं. दोनों मे कारबॉक्सिल अम्ल कार्यात्मक समूह हैं जो कॉपर ऑक्साइड को गलाकार नीचे के शुद्ध कॉपर को फिर से प्रत्यक्ष करते हैं.
CuO + 2RCOOH –> Cu(RCOO)2 + H2O
Blackened copper is basically copper oxide formed with reaction with air. Lemon and tamarind have citric and tartaric acid respectively. Both have carboxylic acid functional group which dissolves the copper oxide and reveals the underlying shining copper.
CuO + 2RCOOH –> Cu(RCOO)2 + H2O
प्र ६) सुधाने तांबे का सिक्का सिल्वर नाइट्रेट के विलयन मे डुबया. थोड़े समय पश्चात उसे वह सिक्का चमकता हुआ दिखा.
क्यों ? संतुलित रसायनिक समीकरण लिखो.
Rusted copper coin is put in silver nitrate solution. After sometime it started to shine. Write balanced equation to describe the reaction.
उ ६) तांबा चाँदी से ज़्यादा क्रियाशील धातु होने के कारण, सिल्वर नाइट्रेट मे तांबे के सिक्के को डुबाने पर विस्थापन अभिक्रिया से विलयन मे कॉपर नाइट्रेट बनता है और चाँदी का सिक्के के उपर अवक्षेपण होता है.
Cu(s) + 2 AgNO3(aq) –> Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 Ag (s)
Copper being more reactive that silver displaces it to dissolve into the solution forming copper nitrate and silver is precipitated out on the coin.
Cu(s) + 2 AgNO3(aq) –> Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 Ag (s)
(Youtube source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P5QlfMRvvF8 )
प्र ७)‘A’धातु का एलेक्ट्रॉनिक समीकरण 2,8,1 है. ‘B’ धातु का एलेक्ट्रॉनिक समीकरण 2,8,8,2 है. कौनसी धातु अधिक क्रियाशील है ? उसे पहचानो. उसकी तनु हाइडरोक्लॉरिक अम्ल के साथ होने वाली अभिक्रिया लिखो.
‘A’ metal has electronic configuration 2,8,1. ‘B’ metal has electronic configuration 2,8,8,2. Which is more reactive? Write its reaction with dilute hydrochloric acid.
उ ७) ‘A’ धातु, जिसमे कुल ११ (२+८+१) एलेक्ट्रान और प्रोटॉन है वो सोडियम है और ‘B’ धातु जिसमे कुल २० (२+८+८+२) एलेक्ट्रान है वो कॅल्षियम है. सोडियम कॅल्षियम से ज़्यादा क्रियाशील है. सोडियम HCl के साथ अभिक्रिया से NaCl लवन और H2 हाइड्रोजन गैस बनता है. 2Na (s) + 2HCl (aq) –> 2NaCl (aq) + H2(g)
‘A’ element that has total 11 (2+8+1) protons and electrons is Sodium and ‘B’ element that has total 20 (2+8+8+2) protons and electrons is Calcium. Sodium is more reactive than Calcium. It reacts with HCl to give NaCl and H2 gas. 2Na (s) + 2HCl (aq) –> 2NaCl (aq) + H2(g)
प्र ८) जस्ते के सल्फ़ाईड से जस्ता प्राप्त करने दो रसायनिक अभिक्रिया होती है. A तथा B के लिए समीकरण लिखो.
Extraction of Zinc from Sulfide involves 2 chemical reactions. Give the products of the reactions.
उ ८) ZnS (भंजन/Roasting): 2 ZnS + 3 O2 –> 2 ZnO + 2 SO2
ZnO (अवकरण/Reduction): 2 ZnO + C → 2 Zn + CO2
प्र ९) निम्न विधानों के रसायनिक समीकरण मे रूपांतरण करके उसे संतुलित करो.
Give chemical reactions which occur under following conditions.
१) अल्यूमिनियम पर से बाश्प प्रवाहित की गई. Water vapour is passed over Aluminium. 2 Al + 3H2O –> Al2O3 + 3H2
२) तांबे का उसके सल्फायड धातु से निष्कर्षण.Extraction of copper from its sulphide. CuS + O2 –> Cu + SO2
३) उष्मा के प्रभाव (Thermit) अभिक्रिया.Thermit reaction. Fe2O3 + 2 Al → 2 Fe + Al2O3
४) अल्यूमिनियम ऑक्साइड, जलीय सोडियम हाइडरॉक्साइड के विलयन मे घुलने से क्या होगा ?
What happens when aluminium oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Al2O3 + 2NaOH –> 2NaAlO2 + H2O
प्र १०) अल्यूमिनियम के निष्कर्षण मे In Aluminium purification
१) बॉक्साइट का सांदीकरण करने के पद्धति का नाम लिखो. Write the name of the method for purification of bauxite.
उ) बॉक्साइट का सांदीकरण करने के पद्धति को बेयर्स प्रोसेस कहते हैं. Purification of bauxite is done by Bayer’s Process.
२) अल्यूमिनियम का विद्युत अपघटनी क्षरण होते समय कॅतोड पर होने वाली अभिक्रिया लिखो.
On electrolytic reduction of aluminium, write the reaction that happens in cathode.
उ) Al+3 + 3 e− → Al
३) क्रायॉलैइट के कार्य तथा सूत्र लिखो. Write the formula and function of cryolite.
उ) क्रायॉलैइट का सूत्र Na3AlF6. कार्य : क्रायॉलैइट अल्यूमिनियम ऑक्साइड को गलाकार विधयुत अपघटन से शुद्ध अल्यूमिनियम प्राप्त करने मे उपयोग होता है.
Cryolite formula: Na3AlF6, Function: Used to dissolve aluminium oxide for electrolytic extraction of aluminium.
४) अल्यूमिनियम हाइडरॉक्साइड पर उष्मा के प्रभाव का संतुलित रसायनिक समीकरण लिखिए.
Write balanced equation for the effect of heat on aluminium hydroxide.
उ) 2 Al(OH)3 –> Al2O3 + 3H2O
५) अल्यूमिनियम निष्कर्षण की नामांकित आकृति बनाओ. Draw diagram of aluminium extraction.

६) समय समय पर एनोड बदलना क्यों आवश्यक है ? Why should anode be changed time to time?
उ) एनोड मे ग्रॅफाइट एलेक्ट्रोड का ऑक्सिजन से अभिक्रिया होकर कार्बन डाइयाक्साइड गॅस बनके ख़तम होते जाता है इसीलिए उनको समय समय पर बदलना ज़रूरी है.
C + O2 –> CO2 (g)
In anode graphite electrode gets consumed by oxygen and goes out as CO2 gas. So it needs to be regularly changed.
C + O2 –>CO2 (g)
७) अल्यूमिनियम के यौगिक को सांद्र कॉस्टिक सोडे के साथ गर्म करने पर क्या होगा? संतुलित रासायनिक समीकरण लिखो.
What happens when aluminium hydroxide is heated with concentrated caustic soda? Write balanced equation.
उ) Al(OH)3 + NaOH –> NaAl(OH)4 –> NaAlO2 + 2H2O
प्र ११) समिश्र मे जंग लगने सा रोकने की दो पद्धतियाँ लिखो. Describe two methods for preventing corrosion of alloys.
उ ११) किसी समिश्र को जंग लगने से रोखने के लिए दो उपाय:
१) गॅल्वनाइज़िंग (Galvanizing) : इसमे लोहा या इस्पात के उपर जसते की परत चड़ाया जाता है, उदाहर्न सुईं, कीलों मे.
२) विद्युत आवरण (Electro-plating): इसमे सोने या चाँदी जैसे क्षरण-मुक्त धातु को विद्युत-अपघटन से छड़ाया जाता है, जैसे गहनों मे.
Corrosion of alloys can be prevented by:
1) Galvanizing: In this method, iron or steel is coated with thin layer of Zinc. Eg. Nails and pins
(Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kwCyq06aatA – American galvanic association)
2) Electroplating: One layer of noble metal is electro-deposited over the alloy eg. Silver and gold plated jewellery
(Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LbpwocW8Rgw – Learning hub academy)
प्र १२) समिश्र अर्थर्थ क्या ? रसायनिक घटकों के साथ दो उदाहरण लिखो.
What are alloys? Give 2 examples with chemical composition.
उ ११) दो या अधिक धातु अथवा एक धातु और एक अधातु इनके निश्चित प्रमाण मे मिश्रण को सम्मिश्रण कहते हैं. जैसे स्टेनलेस स्टील (लोहा, निकल 8%, क्रोमियम 12%) और पीतल (तांबा और जस्ता)
Alloy is a mixture of two or more metals in a range of proportion. Eg. Stainless steel (Iron, Nickel 8% and Chromium 12%) and Brass (Copper and Zinc)
प्र १३) निम्न धातुओं को उनके अभिक्रीयाशीलता के उतरते क्रम मे लिखो. Write in decreasing order of metal reactivity
Cu, Mg, Fe, Na, Ca, Zn
उ १३) Na>Ca>Mg>Zn>Fe>Cu
प्र १४) धातु तथा आधातु मे एलेकट्रोनों का लेनदेन होकर आयनिक यौगिक कैसे बनते हैं, स्पष्ट करो. धातु Mg तथा Cl आधातु इनकी सहायता से उत्तर स्पष्ट करो. Describe how metals and non metals react with exchange of electrons with the help of Mg and Cl as example.
उ १४) धातु अपने संयोजक एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को त्याग कर अपने आवर्त से एक आवर्त पूर्व मे निष्क्रिय गैस का एलेक्ट्रॉनिक संरूपण को प्राप्त करते हैं और घनायन (Cation Mm+) बनते हैं, लेकिन आधातु एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को ग्रहण करके अपने ही आवर्त मे आगे जो निष्क्रिय गैस की आवस्था है, उसे प्राप्त करके श्रवानायन (Anion Xn-) बनते हैं. जब वे आयनिक योगिक बनते हैं तो उस अनुपात मे बनते हैं जिससे योगिक का कुल चार्ज शून्य है, यानी कुल एलेक्ट्रान जो धातु से लिया गया वो अधातु से ग्रहण किया गया. उदाहरण
Mg (2,8,2) –> Mg2+ (2,8) + 2 e–
Cl (2,8,7) + e– –> Cl– (2,8,8)
Metals give away their valence electrons to attain inert gas configuration of the previous period and become a cation Mm+, whereas non-metals gain electrons to attain inert gas configuration of the same period and become and anion Xn-, where ‘m+’ and ‘n-‘ are their oxidation states respectively. When they form ionic compound, they form in such ratio that total charge of the ionic compound is zero, i.e. net electron taken from metals is balanced by electrons gained by non-metals. For example
Mg (2,8,2) –> Mg2+ (2,8) + 2 e–
Cl (2,8,7) + e- –> Cl– (2,8,8) (but since net charge should be balanced two Cl atoms react to give) 2Cl –> 2Cl– + 2e–
Net reaction: Mg2+ + 2Cl– –> MgCl2
प्र १५) ‘X’ तत्व की ऑक्सिजन से अभिक्रिया होकर X2O यह ऑक्साइड बनता है. यह ऑक्साइड पानी से घुलता है तथा इसमे लाल लिटमस नीला होता है. X तत्व धातु है या आधातु एक उदाहरण के साथ स्पष्ट करो.
‘X’ element forms X2O oxide with oxygen. When oxide dissolves in water, it changes red litmus blue. Is ‘X’ a metal or non-metal, explain with example.
उ १५) X2O यौगिक के बनने से, ये जानते हुए की ऑक्सिजन (O) की आक्सिकरण अवस्था -2 है, अतः X की आक्सिकरण अवस्था +1 है. X2O और पानी की अभिक्रिया से जो विलयन है वो लाल लिटमस को नीला कर देता है, यानी X2O एक भस्मिक ऑक्साइड है. इन रसायनिक गुणधर्मों से हमे यह साबित होता है की X एक क्षारीय धातु है. उदाहरण सोडियम (Na):
4 Na + O2 –> 2Na2O, 2Na2O + H2O –> 2NaOH
Since X2O is formed, we know that oxidation state of Oxygen is -2, therefore oxidation state of X is +1. Since X2O reacts with water to change red litmus blue, it must be basic in nature. From the above chemical properties of X, we can conclude that X is a metal from group 1, i.e. an alkali metal.
Eg. 4 Na + O2 –> 2Na2O, 2Na2O + H2O –> 2NaOH
