(1) स्थायी या शाश्वत उपयोग क्या है ? What is sustainable utilization/usage ?
Ans:
(Source: [World from above HD] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fKWQuU0sHPw)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gTamnlXbgqc
शास्वत उपयोग: हमारे प्रकृति के संपत्तियों जैसे पानी, धरती, इर्धन आदि का ऐसा उपयोग जिससे कई 100 सालों तक भी:
– पर्यावरण को कम से कम हानी हो
– प्रदूषण कम से कम हो
– आने वली पीढ़ी के लिए भी वो संपत्ति बना रहे और बचा रहे
Sustainable use: Use of natural resources like water, earth, energy etc in such a way that even of 100s of years:
- There is minimum damage to natural environment (biodiversity)
- There is minimum pollution
- There is enough resources for future generations
(2) स्थायी या शाश्वत विकास के उद्धेश्य क्या है ? What are the goals of sustainable development ?

संयुक्त राष्ट्र द्वारा प्रमाणित लक्ष्य (https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/?menu=1300):
लक्ष्य 1. हर जगह अपने सभी रूपों में गरीबी खत्म करो
लक्ष्य 2. भूखमरी का अंत हो, खाद्य सुरक्षा प्राप्त करें और बेहतर पोषण और टिकाऊ कृषि को बढ़ावा दें
लक्ष्य 3. सभी उम्र के लिए स्वस्थ जीवन सुनिश्चित करें और सभी के कल्याण को बढ़ावा दें
लक्ष्य 4. समावेशी और न्यायसंगत गुणवत्ता की शिक्षा सुनिश्चित करना और सभी के लिए आजीवन सीखने के अवसरों को बढ़ावा देना
लक्ष्य 5. लैंगिक समानता हासिल करना और सभी महिलाओं और लड़कियों को सशक्त बनाना
लक्ष्य 6. सभी के लिए पानी और स्वच्छता की उपलब्धता और टिकाऊ प्रबंधन सुनिश्चित करें
लक्ष्य 7. सभी के लिए सस्ती, विश्वसनीय, टिकाऊ और आधुनिक ऊर्जा तक पहुंच सुनिश्चित करें
लक्ष्य 8. निरंतर, समावेशी और टिकाऊ आर्थिक विकास, पूर्ण और उत्पादक रोजगार और सभी के लिए सभ्य काम को बढ़ावा देना
लक्ष्य 9. लचीला बुनियादी ढांचे का निर्माण, समावेशी और टिकाऊ औद्योगिकीकरण और फोस्टर नवाचार को बढ़ावा देना
लक्ष्य 10. देशों के भीतर और बीच असमानता को कम करें
लक्ष्य 11. शहरों और मानव बस्तियों समावेशी, सुरक्षित, लचीला और टिकाऊ बनाने
लक्ष्य 12. स्थायी उपभोग और उत्पादन पैटर्न सुनिश्चित करें
लक्ष्य 13. जलवायु परिवर्तन और उसके प्रभावों से निपटने के लिए तत्काल कार्रवाई करें
लक्ष्य 14. स्थायी विकास के लिए महासागरों, समुद्रों और समुद्री संसाधनों का संरक्षण और स्थायी रूप से उपयोग करें
लक्ष्य 15. स्थलीय पारिस्थितिकी प्रणालियों के स्थायी उपयोग को सुरक्षित, पुनर्स्थापित और बढ़ावा देने, जंगलों का प्रबंधन, जंगलों का मुकाबला करना, मरुस्थली का मुकाबला करना, भूमि का क्षरण को रोकना और जैव विविधता के नुकसान को रोकना
लक्ष्य 16. स्थायी विकास के लिए शांतिपूर्ण और समावेशी समाजों को बढ़ावा देना, सभी के लिए न्याय प्रदान करना और सभी स्तरों पर प्रभावी, जवाबदेह और समावेशी संस्थाएं बनाना
लक्ष्य 17. कार्यान्वयन के साधनों को मजबूत करना और टिकाऊ विकास के लिए वैश्विक साझेदारी को पुनर्जीवित करना
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals:
- Goal 1. End poverty in all its forms everywhere
- Goal 2. End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture
- Goal 3. Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
- Goal 4. Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
- Goal 5. Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
- Goal 6. Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all
- Goal 7. Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all
- Goal 8. Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
- Goal 9. Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation
- Goal 10. Reduce inequality within and among countries
- Goal 11. Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
- Goal 12. Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
- Goal 13. Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
- Goal 14. Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development
- Goal 15. Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss
- Goal 16. Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels
- Goal 17. Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development
(3) जल संवर्धन के तीन उपाय लिखिए. Give 3 methods for water conservation.
Ans: जल संवर्धन के ३ उपाय:
१) पानी के नाल को ठीक से बंद करना और कम से कम इस्तेमाल करना
२) बारिश के पानी को संग्रह करना और बचाना
३) पेड़ पौधों के आसपास सूखे पत्ते घास आदि से ढक देना ताकि पानी मिट्टी मे जमा रहे.

Methods to conserve water are:
- Closing taps tightly after use and reducing the amount of water needed for daily use.
- Conservation and collection of rain water.
- Mulch around plants to hold water in soil.

(Source: https://www.slideshare.net/elonaanwar/water-conservation-45319066)
(4) दैनिक जीवन मे हम ऊर्जा की बचत कैसे कर सकते हैं ? How can we save energy in our day to day lives ?
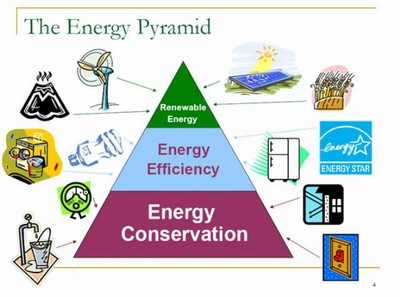
दैनिक ऊर्जा के उपयोग को कम करने के ३ उपाय हैं:
१) ऊर्जा बचत: ज़रूरत ना होने पर विद्युत यंत्रों को बंद कर देना
२) ऊर्जा योग्यता: उन यंत्रों का उपयोग करना जो उसी काम को कम विद्युत उर्जा मे कर देती हैं, उदाहरण Tungsten बल्ब के जगह पर LED का उपयोग
३) अक्षय ऊर्जा स्रोत: सौर उर्जा, वायु उर्जा जैसे साधनों का निर्माण और इस्तेमाल अकरना ताकि कम कार्बन डाइयाक्साइड निर्माण हो.
There are three main ways of saving energy in our day to day lives:
- Energy conservation: Switching off electrical devices when not in use
- Energy efficiency: Using devices that consume less electricity
- Renewable energy: Installing and promoting renewable energy sources like solar power, wind energy etc
(5) जैविक साधन संपत्ति के विनाश के क्या कारण है ? What are the reasons behind destruction of biological resources ?
Ans:
१) उपभोगता, लालच और ‘वायरल’ विकास: पिछले ३०० सालों मे लोगों को यह बहकावे मे लिया गया है की वे जितना ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा समान इस्तेमाल करते हैं, जितना ज़्यादा पैसे कमा और खर्च कर सकते हैं वे उतने ही ‘सफल’ और ‘खुश’ होंगे. इसे उपभोगता कहते हैं. इस सिद्धांत ने मनुष्य को ना ही केवल लालची बन रहा है, बल्कि अब लोगों ने लालच को भी अच्छा मान लिया है. इस वजह से इंसान का ‘विकास’ पर्यावरण के विपरीत होकर हद से ज़्यादा हो रहा है जैसे कोई कैंसर की बीमारी हो गयी हो धरती पर. और उस विकास को कायम रखने के लिए जैविक संपत्तियों का जिस गति से निर्माण होना चाहिए उससे तेज़ गति से नाश हो रहा है.
२) भ्रष्टाचार, दूरदर्शिता की कमी और गैर चक्रीय औद्योगिक व्यवस्था: लगभग सभी बड़े और छोटे औद्योगिक खारखाने, भले वे सरकारी हो या प्राइवेट हो, भ्रष्टाचार से परेशान है और आस पास के पर्यावरण को भी परेशान कर रहा है. भ्रष्ट उद्योगों मे यह सोच विचार नही होता की उनके काम से आगे आने वाले पीढ़ी को क्या नुकसान होगा. उनको बस अपने जेब भरने से मतलब है, सही और दूर दृष्टि नही है. इस वजह से खारकनों या उद्योगों से निकालने वेल प्रदूषित वस्तुओं का पुनरचक्रिकरण या निराकरण नही होता. हलकी परकृति मे कार्बन नाइट्रोजन और अन्य पधार्थ चक्रीय रूप मे प्रवाह करते हैं, इंसान के बनाए खारखाने इस प्राकृतिक नियम का उल्लानगण करते हैं और आस पास के जीव जंतुओं को नुकसान करवाते हैं.
३) प्रदूषण का असर: प्रदूषण के वजह से हवा के रसायनिक संयोजन मे, तापमान मे, समुंदर की अम्लता मे ऐसे सभी प्राकृतिक संतुलन मे पारिवर्तन आ रहा है और ये परिवर्तन जीव जंतों के लिए हानिकारक हो रहा है.
Reason behind destruction of biological resources:
- Consumerism, greed and viral growth:
- Lack of long term vision and non-cyclic industrial culture:
- Pollution:
(6) पर्यावरण चिन्ह क्या है ? What is Eco-mark ?

(India Eco Mark)
ईको मार्क या ईको चिन्ह ब्यूरो ऑफ इंडियन स्टॅंडर्ड्स (BIS) के तरफ से एक प्रमाण चिन्ह है की वो वास्तु को बनाने या इस्तेमाल करने मे पर्यावरण को कम से कम नुकसान पहुँचता हो. यह १९९१ मे शुरू हुआ. ईको मार्क के एक उद्धसी ये भी था की ग्राहकों को पर्यावरण को लेकर जागरूकता बढ़ें. यह मार्क अलग अलग वस्तुओं सामग्रियों मे होता है और आने वेल वस्तुओं के उत्पादन के लिए भी एक मार्ग दर्शक होता है. अलग अलग देशों का अलग अलग ईको-मार्क होता है.
Ecomark or Eco mark is a certification issued by the Bureau of Indian Standards to products conforming to a set of standards aimed at the least impact on the ecosystem. The marking scheme was started in 1991. One of the purposes of the mark is increasing awareness among the consumers towards reducing environment impact. The mark is issued to various product categories and the development of standards for more products is in progress. Different countries have different eco-marks.



(7) पुनरचक्रिकरण क्या है ? कोई एक उदाहरण दीजिए. What is recycling. Give two examples.
- Recycling of rain water after filtration.
- Plastic bottles can be recycled to make new products like comb, chairs etc.
(8) हमारे संविधान मे पर्यावरण के लिए दिए गये प्रावधान को स्पष्ट कीजिए. Describe the provisions given in our constitution for the environment.
Environmental protection is a fundamental duty of every citizen of this country under Article 51-A(g) of our Constitution which reads as follows,
“It shall be the duty of every citizen of India to protect and improve the natural environment including forests, lakes, rivers and wildlife and to have compassion for living creatures.”
Right to environment is also a right without which development of individual and realisation of his or her full potential shall not be possible. Articles 21, 14 and 19 of this part have been used for environmental protection.
According to Article 21 of the constitution, “no person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to procedure established by law”.
Article 48 -A of the constitution says that “the state shall endeavor to protect and improve the environment and to safeguard the forests and wild life of the country”.
Article 47 provides that the State shall regard the raising of the level of nutrition and the standard of living of its people and the improvement of public health as among its primary duties. The improvement of public health also includes the protection and improvement of environment without which public health cannot be assured.
The constitution of India embodies the framework of protection and preservation of nature without which life cannot be enjoyed. The knowledge of constitutional provisions regarding environment protection is need of the day to bring greater public participation, environmental awareness, environmental education and sensitize the people to preserve ecology and environment.
(9) पर्यावरण के लिए प्रत्येक नागरिक का मौलिक कर्तव्य क्या है ? What are the fundamental duties of every citizen towards environment ?
(10) जलप्रदूषण नियंत्रण के लिए MPCB के दो कार्य बताएँ. Give two works of Maharashtra Pollution Control Board for preventing water pollution.
(11) WBCSD के कार्य बताएँ. List the works of WBCSD.

