इस लेखन मे 10 वी कक्षा का पहला अध्याय “तत्वों की पाठशाला” प्रश्नोत्तर लिखे गये हैं. संधर्भ के लिए पाठ पुस्तक, तत्व ताश, और आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी का भी उपयोग करें.
This is the post for sharing the question and answers of Chapter-1, School of Elements. Given below are the questions. Consult your textbook, periodic cards and modern periodic table as a reference.
स्वाध्याय के लिए वीडियो लेक्चर्स (Video lectures for self learning) :
Part 1: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hCnbNdpqpGE
Part 2: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K6eYkHlez9M
Part 3: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q-j1GPmLguE&t=6s
Revision: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MCHf8bgEMl8&t=26s
एक बार प्रश्नों के उत्तर खुद से लिखने की कोशिश करें. उसके बाद उत्तर के लिए नीचे स्क्रोल करें.
Once you have given your best attempt, you can slide down further for the answers.
प्रश्नोत्तर 10-वी कक्षा (महाराष्ट्रा शिक्षण-मंडल) Self-learn 10th standard (Maharashtra Board)
1) तत्वों की पाठशाला School of elements
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
प्रश्न Questions
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
१) रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो Fill in the blanks:
१) ‘M’ धातु के क्लॉराइड का अणुसूत्र MCl2 है. तो M ___________ समूह का कोई भी तत्व हो सकता है.
1) ‘M’ metal chloride’s formula is MCl2. Then, M can be any element of ______ group.
२) ‘M’ धातु के फ्लोराइड का अणुसूत्र MF है. तो M ___________ समूह का कोई भी तत्व हो सकता है.
2) ‘M’ metal fluoride’s formula is MF. Then, M can be any element of ______ group.
३) आवर्त सारणी मे __________ समूह के सभी तत्व सामान्य तापमान और दाब पर गैसीय अवस्था मे पाए जाते हैं.
3) In periodic table, _______ group’s elements are found in gaseous state at room temperature and pressure.
४) तत्वों को तीन तीन के समूह मे व्यवस्थित करने को ______ कहते हैं.
4) Method of arranging elements in groups of 3-3 is called as __________________.
५) न्यूलॅंड ने तत्वों को व्यवस्थित रखने के लिए जिस नियम का उपयोग किया था उसे ___________ नियम कहते हैं.
5) Newland’s method of arranging the elements of periodic table is known as law of __________ .
६) मेंडेलीव की आवर्त सारणी मे एका-अल्यूमिनियम और एका-बोरों तत्वों को आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे __________ और __________ कहा जाता है.
6) In Mendeleev’s periodic table, eka-aluminium and eka-boron are called as _________ and ____________ elements in modern periodic table.
७) अगर एक तत्व का विद्युतृणात्मकता अधिक है, याने रसायनिक बंधन बनाने वाले एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को अपने तरफ आकर्षित करने की, वो एक _________ ( धातु / आधातु ) है. अगर उस तत्व का गुण एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को त्यागने की है, याने विद्युतृणात्मकता कम है, वो एक ________ है.
7) If an element has high electronegativity, i.e. tendency to attract bonding electrons towards itself, it would be a __________ (metal/non-metal). If the element has tendency to give away electrons, i.e. having low electronegativity,it is a ___________. (metal/non-metal)
8) जो तत्व धातु एवं अधातु दोनों के गुणधर्म प्रदर्शित करते हैं उन्हे ______________ कहते हैंउदाहरण ____________ और _____________.
8) Elements that display both metallic and non-metallic properties are known as ___________, for example ___________ and _____________.
9) अल्यूमिनियम के _________ संयोजक एलेक्ट्रॉन्स हैं, __________ उसकी संयोजकता है, वो _____ एलेक्ट्रॉन्स दे देता है इसीलिए उसकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था _____ है. वो एक ________ है.
9) Aluminium has _________ valence electrons, __________ as valency; it gives away _____ electrons and thus has oxidation state of _______. It is a ________.
10) नाइट्रोजन के _________ संयोजक एलेक्ट्रॉन्स हैं, __________ उसकी संयोजकता है, वो _____ एलेक्ट्रॉन्स दे देता है इसीलिए उसकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था _____ है. वो एक ________ है.
10) Nitrogen has ___________ valence electrons, _________ as valency, it can take ______ electrons and thus has oxidation state of _______. It is a __________.
११) हर कोई तत्व रसायानीक प्रक्रिया से एलेक्ट्रॉन्स का लें-दें या बटवारा करके _________ तत्वों के संरूपण को पाने की कोशिश करते हैं.
11) Any element, by chemical reactions in the form of giving-taking or sharing electrons, tries to attain electronic configuration of ____________ elements.
१२) दो धातु आपस मे _________ रसायनिक बँध बनाते हैं, दो आधातु आपस मे _____________ बँध बनाते हैं और धातु और आधातु आपस मे _________ बँध बनाते हैं.
12) Two metals together form __________ bond, two non-metals form ___________ bond and a metal and non- metal forms ____________ bond.
प्र २) वैज्ञानिक कारण लिखिए Give scientific reasons
१) समूह मे नीचे की ओर जाते समय परमाणुओं का आकार बढ़ता जाता है.
1) Within a group when we go downwards, element size increases.
२) आवर्त मे बाईं ओर से दाहिनी ओर जाने पर धात्विक गुणधर्म कम होते हैं.
2) In a period, on moving from left to right, metallic properties decrease.
३) समान समूह के तत्वों की संयोजकता समान होती है.
3) Elements in same group has same valency.
४) आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे समूह १८ के तत्व निष्क्रिय हैं, यानी रसायनिक प्रक्रिया मे भाग नही लेते.
4) In modern periodic table group 18 elements are inert, and they don’t take part in chemical reactions.
५) Na का ऑक्साइड Na2O है, Mg का ऑक्साइड MgOहै, और Al का Al2O3.
5) ‘Na’ oxide is Na2O, ‘Mg’ oxide is MgO, and Al oxide is Al2O3.
3) उचित जोड़ियाँ लगाओ Make correct pairs
| Element तत्व | Classification वर्गीकरण |
| सोडियम (Sodium)-11 | निसक्रिय गैस (Inert gas) |
| सलफर (Sulphur)-16 | संक्रमण धातु (Transition metal) |
| आर्गॉन ( Argon)-18 | आंतरिक संकरमण धातुलॅंतनाइड (Inner transition metal – Lanthanide) |
| मॅंगनीस (Manganese)-25 | सामान्य धातु ( Common metal) |
| सीरियम (Cerium)-58 | अधातु(Non-metal) |
| युरेनीयम (Uranium)-92 | धातुसदृश (Metalloid) |
| बोरों (Boron)-5 | आंतरिक संकरमण धातुअक्टिनाइड ( Inner transition metal – Actinide) |
प्र ४ संक्षेप मे उत्तर लिखिए Write short answers
१) वर्गीकरण से आप क्या समझते हैं. वर्गीकरण का आवर्त सारणी से क्या संबंध है.
1) What do you understand by classification? What is role of classification in periodic table of elements?
२) मेंडेलीव की आवर्त सारणी के खूबियाँ और दोष लिखिए. उन दोषों को आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे कैसे दूर किया गया है.
2) Give merits and demerits of Mendeleev periodic table. How the demerits are removed in modern periodic table?
३) आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी के प्रथम २० तत्वों का एलेक्ट्रॉनिक संरूपण लिखिए. इनमे कौँसे धातु, अधातु और धातुसदृश हैं ?
3) Give electronic configuration of first 20 elements. Which among these are metals, non-metals and metalloids?
४) परमाणु आकार और विद्युतृणात्मकता से आप क्या समझते हैं? वे आवर्त सारणी मे कैसे बदलते हैं, स्पष्ट करो.
4) What do you understand by atomic size and electronegativity? How do they change in periodic table? Explain.
5) इन तत्वों के नाम लिखें Give names for :
1) 3 तत्व जिनके संयोजक कक्षा मे केवल १ एलेक्ट्रान हैं. 3 elements which has only one electron in valence shell.
2) 3 तत्व जिनके संयोजक कक्षा मे २ एलेक्ट्रान हैं. 3 elements which have 2 electrons in valence shell.
3) 3 तत्व जिनके संयोजक कक्षा मे ३ एलेक्ट्रान हैं. 3 elements with 3 electrons in valence shell.
4) 3 तत्व जिनके संयोजक कक्षा मे ४ एलेक्ट्रान हैं.3 Elements with 4 electrons in valence shell.
5) 3 तत्व जिनकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था -३ है, संयोजक कक्षा कुल ८ मे से ५ एलेक्ट्रान हैं. 3 Elements with oxidation state of -3, having 5 out of 8 electrons in valence shell.
6) 3 तत्व जिनकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था -२ है, संयोजक कक्षा कुल ८ मे से ६ एलेक्ट्रान हैं. 3 elements with oxidation state -2, having 6 out of 8 electrons in valence shell.
7) 3 तत्व जिनकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था -१ है, संयोजक कक्षा कुल ८ मे से ७ एलेक्ट्रान हैं. 3 elements with oxidation state -1, having 7 out of 8 electrons in valence shell.
8) ३ तत्व जिनकी संयोजक कक्षा भारी हुई है, जिससे वे रसायनिक प्रक्रिया मे भाग नही लेते. 3 elements which do not react as they have complete valence shell.
9) आवर्त १ के दो तत्व.2 elements of period 1.
10) आवर्त २ के ८ तत्व.8 elements of period 2.
11) आवर्त ३ के ८ तत्व.8 elements of period 3.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
उत्तर Answers
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
१) रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो Fill in the blanks:
१) ‘M’ धातु के क्लॉराइड का अणुसूत्र MCl2 है. तो M 2nd (भूक्षारीय धातु) समूह का कोई भी तत्व हो सकता है.
1) ‘M’ metal chloride’s formula is MCl2. Then, M can be any element of 2nd (Alkaline earth metal) group.
२) ‘M’ धातु के फ्लोराइड का अणुसूत्र MF है. तो M 1st (क्षारीय धातु) समूह का कोई भी तत्व हो सकता है.
2) ‘M’ metal fluoride’s formula is MF. Then, M can be any element of 1st (Alkali metals) group.
३) आवर्त सारणी मे 18th (निष्क्रिय गैस) समूह के सभी तत्व सामान्य तापमान और दाब पर गैसीय अवस्था मे पाए जाते हैं.
3) In periodic table, 18th (inert gases) group’s elements are found in gaseous state at room temperature and pressure.
४) तत्वों को तीन तीन के समूह मे व्यवस्थित करने को त्रिक (डोबेरायनेर) कहते हैं.
4) Method of arranging elements in groups of 3-3 is called as (Doberiener’s) triad.
५) न्यूलॅंड ने तत्वों को व्यवस्थित रखने के लिए जिस नियम का उपयोग किया था उसे अष्टक नियम कहते हैं.
5) Newland’s method of arranging the elements of periodic table is known as law of octaves .
६) मेंडेलीव की आवर्त सारणी मे एका–अल्यूमिनियम और एका–बोरों तत्वों को आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे गॅलियम, और जरमेनीयम कहा जाता है.
6) In Mendeleev’s periodic table, the predicted elements eka-aluminium and eka-silicon that were later discovered are called as gallium and germanium in modern periodic table.
७) अगर एक तत्व का विद्युतृणात्मकता अधिक है, याने रसायनिक बंधन बनाने वाले एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को अपने तरफ आकर्षित करने की, वो एक अधातु ( धातु / अधातु ) है. अगर उस तत्व का गुण एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को त्यागने की है, याने विद्युतृणात्मकता कम है, वो एक धातु है.
7)If an element has high electronegativity, i.e. tendency to attract bonding electrons towards itself, it would be a non-metal (metal/non-metal). If the element has tendency to give away electrons, i.e. having low electronegativity,it is a metal. (metal/non-metal)
8) जो तत्व धातु एवं अधातु दोनों के गुणधर्म प्रदर्शित करते हैं उन्हे धातुसदृश कहते हैं उदाहरण बोरोन और सिलिकॉन.
8) Elements that display both metallic and non-metallic properties are known as metalloids, for example boron and silicon.
9) अल्यूमिनियम के 3 संयोजक एलेक्ट्रॉन्स हैं, उसकी संयोजकता 3 है, वो 3 एलेक्ट्रॉन्स दे देता है इसीलिए उसकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था +3 है. वो एक धातु है.
9) Aluminium has 3 valence electrons, 3 as valency; it gives away 3 electrons and thus has oxidation state of +3. It is a metal.
10) नाइट्रोजन के 5 संयोजक एलेक्ट्रॉन्स हैं, उसकी संयोजकता 3 है, वो 3 एलेक्ट्रॉन्स लेता है, इसीलिए उसकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था -3 है. वो एक अधातु है.
10) Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, 3 as valency, it can take 3 (8-5) electrons and thus has oxidation state of -3. It is a non-metal.
११) हर कोई तत्व रसायानीक प्रक्रिया से एलेक्ट्रॉन्स का लें-दें या बटवारा करके निष्क्रिय गैस तत्वों के संरूपण को पाने की कोशिश करते हैं.
11) Any element, by chemical reactions in the form of giving-taking or sharing electrons, tries to attain electronic configuration of inert elements.
१२) दो धातु आपस मे धात्विक बँध बनाते हैं, दो अधातु आपस मे सहसंयोजक बँध बनाते हैं और धातु और अधातु आपस मे आयनिक बँध बनाते हैं.
12) Two metals together form metallic bond, two non-metals form covalent bond and a metal and non- metal can form ionic bond.
प्र २) वैज्ञानिक कारण लिखिए Give scientific reasons
१) समूह मे नीचे की ओर जाते समय परमाणुओं का आकार बढ़ता जाता है.
1) Within a group when we go downwards, element size increases.
किसी समूह मे उपर से नीचे जाने पर, एलेक्ट्रान के कक्षाओं की संख्या बदती जाती है, आखरी कक्षा नाभि से सबसे दूर होता है. इसीलिए परमाणु त्रिज्या बढ़ता है.
Within a group when we go downwards, the number of shells of electronic orbital increases, the last shell being farther away from the nucleus. So the atomic size increases.
२) आवर्त मे बाईं ओर से दाहिनी ओर जाने पर धात्विक गुणधर्म कम होते हैं.
2) In a period, on moving from left to right, metallic properties decrease.
एक ही आवर्त मे बाएँ से दाएँ बढ़ने पर, बाहर्तम सययोजक कक्षा तो वो ही है लेकिन नाभि मे प्रोटॉन्स की संख्या बढ़ जाती है. इस विद्युत बल से नाभि बाहर्तम एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को और भी ज़ोर से खींचता है, जिससे इलेक्ट्रोंस को त्यागने की संभावना कम होती जाती है. इलेक्ट्रॉन त्यागना ही धात्विक गुणधर्म है. दाहिनी ओर के तत्व इलेक्ट्रॉन के लेने या बाँटने से अपने संयोजक कक्षा को पूर्ण करते हैं. इसीलिए एक ही आवर्त मे बाएँ से दाएँ बढ़ने पर धात्विक गुणधर्म घटता जाता है.
When we move within a period, the outermost shell is the same but number of protons (atomic number) increases. This makes the nucleus attract the outer electrons more strongly, thus reducing the tendency of the atom to give away electrons which is the characteristic metallic property. Atoms on far right try to fulfil its octet by gaining or sharing electrons. So, the metallic properties decrease as we move from left to right in a period.
३) समान समूह के तत्वों की संयोजकता समान होती है. 3) Elements in same group has same valency.
आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे एक ही समूह के सभी तत्वों के बाहर्तम कक्षा (संयोजक कक्षा) मे एलेक्ट्रान की संख्या एक समान होता है इसीलिए वे सब एक ही तरह से उनके एलेकट्रोनों का लें दें या बाँटते है, याने उनकी संयोजकता एक समान है.
Elements of the same group have same number of electrons in their outermost shell. Since the outermost shell is the only shell which takes part in a chemical reaction, all elements of the same group have same tendency to give, take or share electrons i.e. same valency.

(Source: https://www.learner.org/courses/chemistry/images/text_img/ValenceElectronPatterns.jpg)
४) आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे समूह १८ के तत्व निष्क्रिय हैं, यानी रसायनिक प्रक्रिया मे भाग नही लेते.
4) In modern periodic table group 18 elements are inert, and they don’t take part in chemical reactions.
१८ वे समूह के तत्व सभी के बाहर्तम कक्षा पूर्ण रूप से भरा हुआ है. वे किसी इलेक्ट्रॉन को इसीलिए देना, लेना या बाँटना नही चाहते, और रसायनिक अभिक्रियाओं मे भाग नही लेते.
Elements in the 18th group of modern periodic take have complete outermost electron shell. So they are chemically highly stable and don’t wish to give, take or share electrons by taking part in chemical reactions.
५) Na का ऑक्साइड Na2O है, Mg का ऑक्साइड MgO है, और Al का Al2O3. 5) ‘Na’ oxide is Na2O, ‘Mg’ oxide is MgO, and Al oxide is Al2O3.

तत्वों की आक्सिकरण अवस्था निर्णय करता है कैसे परस्पर यौगिक बनेंगे Oxidation state of the elements decide the nature of the compound formed between them
(Source: https://namakiri.files.wordpress.com/2013/03/screen-shot-2013-03-27-at-12-51-09-pm.png)
‘Na’ याने सोडियम, जिसका परमाणु क्रमांक ११ है, और इलेक्ट्रॉनिक संरूपण (२,८,१) है, वह एक एलेक्ट्रान देकर निष्क्रिय अवस्था पा सकता है. मॅग्नीज़ियम ‘Mg’-12, का इलेक्ट्रॉनिक संरूपण (२,८,२) है, वह २ इलेक्ट्रॉन देकर निष्क्रिय अवस्था पा सकता है और अल्यूमिनियम Al-13, (२,८,३) टीन इलेक्ट्रॉन देकर. ऑक्सिजन , O-8 (२,६), संयोजक कक्षा मे २ इलेक्ट्रोनों को ले सकता है.
जब धातु और अधातु मे बन्ध बनते हैं, तो धातुओं के द्वारा दिए गये इलेक्ट्रॉन की संख्या और अधातुओं द्वारा लिए गये एलेक्ट्रान की संख्या एक समान होती है.
Na के दो अणु कुल २ एलेक्ट्रान (2 x 1e- =2e-) देते हैं, ऑक्सिजन का एक अणु उसे लेता है(1 x 2e- = 2e-) और Na2O बनता है.
Mg का एक अणु २ इलेक्ट्रॉन देता है (1 x 2e- = 2e- ) और ऑक्सिजन का एक अणु उसे लेता है(1 x 2e- = 2e-), MgO बनता है.
Al के २ अणु कुल 6 इलेक्ट्रॉन देते हैं (2 x 3e- = 6e-) जिसे ऑक्सिजन के ३ अणु ले लेते हैं (3 x 2e- = 6e-), Al2O3 बनता है.
Sodium-11 has (2,8,1) i.e. one electron in outermost shell. It can give 1 electron to gain octet of the previous shell.
Magnesium-12 with (2,8,2) i.e. have 2 electrons to give and alumimium-13 (2,8,3) has 3 electrons to give.
When a compound is formed net electrons given by metals should be equal to net electrons taken by non-metals (oxygen). Oxygen-8, with electronic configuration (2,6) in outermost shell needs to gain 2 electrons to fulfil its octet.
Therefore it needs 2 sodium atoms (2 x 1e– = 2e–) to give 2 electrons to one oxygen atom (1 x 2e– = 2e–) to form Na2O.
One Mg atom gives 2 electrons ( 1 x 2e– = 2e–) to one oxygen atom which gains it (1 x 2e– = 2e–) to form MgO.
Two aluminium atoms can give 6 electrons ( 2 x 3e– = 6e–) to three oxygen atoms (3 x 2e– = 6e–) to form Al2O3.
3) उचित जोड़ियाँ लगाओ Make correct pairs
| Element तत्व | Classification वर्गीकरण | Element तत्व | Classification वर्गीकरण |
| सोडियम (Sodium)-11 | निसक्रिय गैस
(Inert gas) |
सोडियम (Sodium)-11 | सामान्य धातु
( Common metal) |
| सलफर (Sulphur)-16 | संक्रमण धातु
(Transition metal) |
सलफर (Sulphur)-16 | आधातु
(Non-metal) |
| आर्गॉन ( Argon)-18 | आंतरिक संकरमण धातुलॅंतनाइड
(Inner transition metal – Lanthanide) |
आर्गॉन ( Argon)-18 | निसक्रिय गैस
(Inert gas) |
| मॅंगनीस (Manganese)-25 | सामान्य धातु
( Common metal) |
मॅंगनीस (Manganese)-25 | संक्रमण धातु
(Transition metal) |
| सीरियम (Cerium)-58 | आधातु
(Non-metal) |
सीरियम (Cerium)-58 | आंतरिक संकरमण धातुलॅंतनाइड
(Inner transition metal – Lanthanide) |
| युरेनीयम (Uranium)-92 | धातुसदृश
(Metalloid) |
युरेनीयम (Uranium)-92 | आंतरिक संकरमण धातुअक्टिनाइड
( Inner transition metal – Actinide) |
| बोरों (Boron)-5 | आंतरिक संकरमण धातुअक्टिनाइड
( Inner transition metal – Actinide) |
बोरों (Boron)-5 | धातुसदृश
(Metalloid) |
प्र ४) संक्षेप मे उत्तर लिखिए Write short answers
१) वर्गीकरण से आप क्या संजते हैं. वर्गीकरण का आवर्त सारणी से क्या संबंध है.
1) What do you understand by classification? What is role of classification in periodic table of elements?
हम एक बड़े और जटिल समूह के सदस्यों को अपने गुणधर्म के अनुसार कई सरल समूहों मे विभाजित करते हैं. इससे अब उनको समजना आसान हो जाता है. किसी एक समूह के सदस्यों मे, या किन्ही दो समूहों के बीच मे जो संबंध है, वो हमे वर्गीकरण के मदद से नज़र आने लगता है. हम इन समूहों की जानकारी से अब तक अंजान सदस्यों के बारे मे भी भविष्यवाणी कर सकते हैं.
आवर्त सारणी मे तत्वों को परमाणु करमांक के बढ़ते क्रम मे रखा गया है और उनके इलेक्ट्रॉनिक संरूपण के हिसाब से वर्गीकरण किया गया है. एक ही समूह के तत्वों का रसायनिक गुणधर्म एक समान है और एक ही आवर्त के तत्वों की संयोजक ( बाहर्तम कक्षा) समान होता है.
We classify one complex large group into simple smaller groups based on common properties of the members. That makes it easy to understand. We can observe possible co-relations between the groups and within the group. We can also make correct predictions about hitherto unknown members of the group.
In periodic table of elements, the elements are arranged in increasing atomic number and classified based on their electronic configuration thus elements of same group have same outermost electronic configuration and chemical properties, and elements in the same period has same outermost shell number.
२) मेंडेलीव की आवर्त सारणी के खूबियाँ और दोष लिखिए. उन दोषों को आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे कैसे दूर किया गया है.
2) Give merits and demerits of Mendeleev periodic table. How the demerits are removed in modern periodic table?
|
मेंडेलीव की आवर्त सारणी के दोष Demerits of Mendeleev’s periodic table |
आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे के उपाय Solutions in modern periodic table |
| हाइड्रोजन, क्षारीय धातुओं तथा हालजन दोनों के साथ समानता रखता है. इसीलये उसका कोई निश्चित स्थान नही है.
Hydrogen shows similarity with both alkali metals and halogens. Therefore it does not have fixed spot. |
हाइड्रोजन को क्षारीय धातुओं के साथ रखा गया है क्योंकि उसके आकरी कक्षा के ‘s’ उपकक्षा मे एक ही एलेक्ट्रान है.
Hydrogen is grouped with alkali metals in group 1 as it has only one electron is s shell. |
| एक ही तत्व के विभिन्न परमाणु भार वाले अणु रसायनिक दृष्टि से समान हैं, उन्हे एक ही स्थान मे रखना आवश्यक हैं.
Atoms of same element with different atomic masses are chemically same, so they are kept in same place. |
आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी प्रोटॉन के क्रमांक पर आधारित है, परमाणु भार पर नही, इसीलिए समस्थानिक जिनके प्रोटॉन संख्या एस समान है, रसायनिक गुणधर्म भी एक समान है और वे एक ही साथ रखे गये हैं.
Since modern periodic table is based on proton number, not atomic mass, isotopes have same proton number giving same chemical properties so grouped together. |
| कुछ स्थानों पर अधिक परमाणु भर वाले कुछ तत्वों को कम परमाणु भार वाले तत्वों के पहले रखा गया है.(Co, Ni)
In some places, elements with higher atomic mass are kept before lighter element to match chemical nature. |
परमाणु करमांक के आरोही क्रम पर आधारित आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे Co और Ni रसायनिक गुणधर्म के अनुसार भी सही क्रम मे रखा गया है. (परमाणु क्रमांक Co<Ni, लेकिन परमाणु भार Co>Ni)
Arrangement based on increasing atomic number for Co and Ni gives correct order for chemical nature as well. (परमाणु क्रमांक Co<Ni, लेकिन परमाणु भार Co>Ni) |
| कुछ आसमान गुणधर्म वाले कुछ तत्वों को एक ही उपसमूह मे रखा गया है. जैसे Mn को हालजन मे.
Some dissimilar elements are kept in same subgroup, for example Mn with halogens. |
आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी मे असमान तत्वों को एक साथ रखने का कोई दुविधा नही है. मॅंगनीस संक्रमण तत्वों मे आता है, ना के हेलोजॅन मे.
No such issues in modern periodic table, Mn is kept along with transition metals, not halogens. |
३) आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी के प्रथम २० तत्वों का एलेक्ट्रॉनिक संरूपण लिखिए. इनमे कौँसे धातु, अधातु और धातुसदृश हैं ?
3) Give electronic configuration of first 20 elements. Which among these are metals, non-metals and metalloids?
प्रोटॉन संख्याProton No. |
नामName |
एलेक्ट्रॉनिक संरूपणElectronic configuration |
कक्षीय विन्यासOrbital configuration |
धातु / अधातुMetal/Non-metal
|
|||
| 1 (H) | हाइड्रोजन
Hydrogen |
1
|
1s1 | Non Metal
अधातु |
|||
| 2 (He) | हीलियम
Helium |
2
|
1s2 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| पहला आवर्त समाप्त दूसरा आवर्त शुरू
1st period complete, 2nd period start |
|||||||
| 3 (Li) | लिथियम
Lithium |
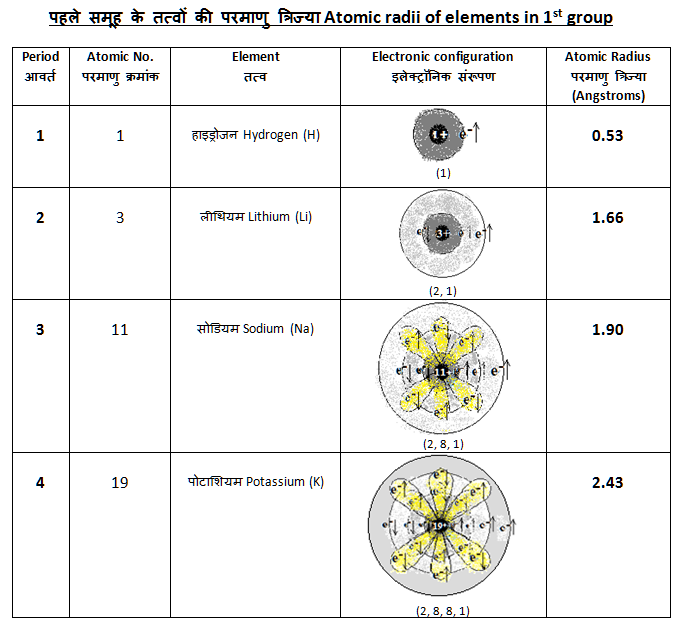
2,1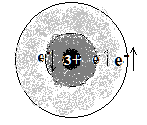 |
1s2 2s1 | धातु
Metal |
|||
| 4 (Be) | बेरीलियम
Beryllium |
2,2 |
1s2 2s2 | धातु
Metal |
|||
| 5 (B) | बोरों
Boron |
2,3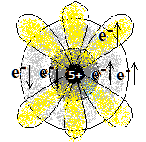 |
1s2 2s2 2p1 | धातुसदृश
Metalloid |
|||
| 6 (C) | कार्बन
Carbon |
2,4 |
1s2 2s2 2p2 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| 7 (N) | नाइट्रोजन
Nitrogen |
2,5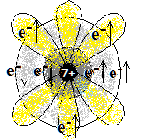 |
1s2 2s2 2p3 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| 8 (O) | ऑक्सिजन
Oxygen |
2,6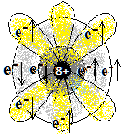 |
1s2 2s2 2p4 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| 9 (F) | फ्लुरिन
Fluorine |
2,7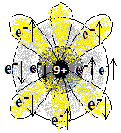 |
1s2 2s2 2p5 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| 10 (Ne) | नीयान
Neon |
2,8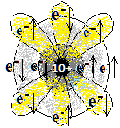 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| दूसरा आवर्त समाप्त तीसरा आवर्त शुरू
Second period complete, Third period start |
|||||||
| 11 (Na) | सोडियम
Sodium |
2,8,1 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 | धातु
Metal |
|||
| 12 (Mg) | मॅग्नीज़ियम
Magnesium |
2,8,2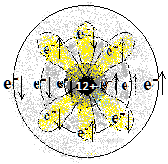 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 | धातु
Metal |
|||
| 13 (Al) | अल्यूमिनियम Aluminium | 2,8,3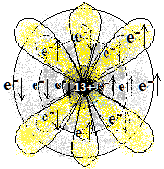 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 | धातु
Metal |
|||
| 14 (Si) | सिलिकन
Silicon |
2,8,4 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 | धातुसदृश
Metalloid |
|||
| 15 (P) | फॉस्फरस
Phosphorus |
2,8,5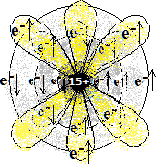 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| 16 (S) | सल्फर
Sulphur |
2,8,6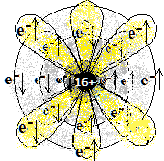 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| 17 (Cl) | क्लोरिन
Chlorine |
2,8,7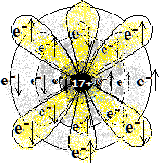 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| 18 (Ar) | आर्गॉन Argon | 2,8,8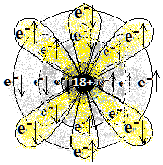 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 | अधातु
Non-metal |
|||
| तीसरा आवर्त समाप्त चौथा आवर्त शुरू
3rd period complete, 4th period start |
|||||||
| 19 (K) | पोटाशियम
Potassium |
2,8,8,1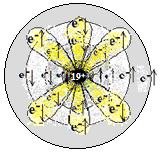 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 | धातु
Metal |
|||
| 20 (Ca) | कॅल्षियम
Calcium |
2,8,8,2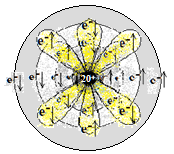 |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 |
धातु
Metal |
|||
४) परमाणु आकार और विद्युतृणात्मकता से आप क्या समजते हैं? वे आवर्त सारणी मे कैसे बदलते हैं, स्पष्ट करो.
4) What do you understand by atomic size and electronegativity? How do they change in periodic table? Explain.
परमाणु आकार परमाणु त्रिज्या से ज्ञात होता है, जो की नाभिक केंद्र से सबसे बाहर्तम इलेक्ट्रॉनिक कक्षा के बीच की दूरी हैं. किसी समूह मे उपर से नीचे जाने पर, एलेक्ट्रान के कक्षाओं की संख्या बदती जाती है, आखरी कक्षा परमाणु का बीर्जकेंद्र से सबसे दूर होता है. इसीलिए परमाणु त्रिज्या बढ़ता है. एक ही आवर्त मे बाएँ से दाएँ बढ़ने पर, बाहर्तम सययोजक कक्षा तो वोही है लेकिन नाभि मे प्रोटॉन्स की संख्या बढ़ जाती है. इस वजह से परमाणु का बीर्जकेंद्र, विद्युत बल से, बाहर्तम एलेक्ट्रॉन्स को और भी ज़ोर से खींचता है, और परमाणु त्रिज्या कम हो जाता है.
Distance between the nucleus of the atom to its outermost electron shell is known as atomic radius which is the measure of atomic size. On moving from top to bottom within a group, number of electron shells increase, the last shell being farthest from the nucleus, so atomic size increases. On moving from left to right within a period, number of protons increases but the outermost electron shell remains the same, thereby increasing the attractive electric force of nucleus over its outermost electrons, thus atomic size decreases.
(Source: https://ch301.cm.utexas.edu/svg/atomic-radii.svg)
वैद्युतीयऋणात्मकता किसी भी तत्व के बँध मे होने वाले इलेक्ट्रॉन को अपने ओर आकर्षित करने की क्षमता को दर्शाता है. वैद्युतीयऋणात्मकता किसी समूह मे उपर से नीचे जाने पर कम होता जाता है क्योंकि परमाणु आकर बढ़ने पर केंद्र का बल, बाहर्तम कक्षा के इलेक्ट्रॉन पर, कम होता जाता है. किसी आवर्त मे बाएँ से दाएँ जाने पर प्रोटॉन का क्रमांक बढ़ता है, जिससे नाभिक केंद्रीय बल बढ़ता है,और वैद्युतीयऋणात्मकता बढ़ता है.
Electronegativity refers to the ability of the atom to pull electrons towards itself within a bond. From top to bottom within a group, electronegativity decreases as atomic size increases and the outer electron shell farther away from the nucleus.
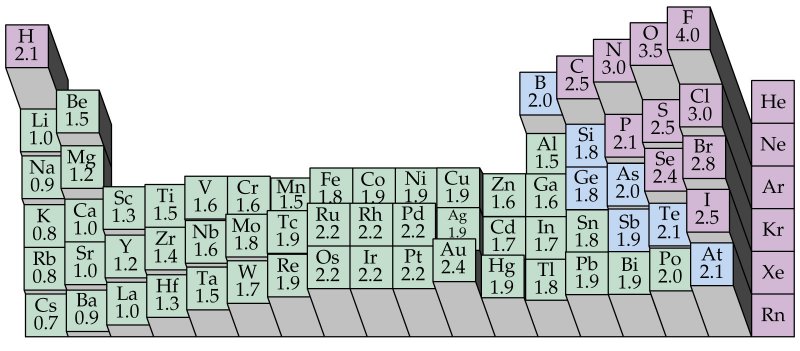
(Source: https://usflearn.instructure.com/courses/986898/files/31116524)
5) Give names for:
1) 3 तत्व जिनके संयोजक कक्षा मे केवल १ एलेक्ट्रान हैं. 3 elements which has only one electron in valence shell.
H-1, Li-3, Na-11
2) 3 तत्व जिनके संयोजक कक्षा मे २ एलेक्ट्रान हैं. 3 elements which have 2 electrons in valence shell.
Be-4, Mg-12 & Ca-20
3) 3 तत्व जिनके संयोजक कक्षा मे ३ एलेक्ट्रान हैं. 3 elements with 3 electrons in valence shell.
B-5, Al-13 & Ga-31
4) 3 तत्व जिनके संयोजक कक्षा मे ४ एलेक्ट्रान हैं.3 Elements with 4 electrons in valence shell.
C-6, Si-14 & Ge-32
5) 3 तत्व जिनकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था -३ है, संयोजक कक्षा कुल ८ मे से ५ एलेक्ट्रान हैं.
3 Elements with oxidation state of -3, having 5 out of 8 electrons in valence shell.
N-7, P-15 & As-33
6) 3 तत्व जिनकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था -२ है, संयोजक कक्षा कुल ८ मे से ६ एलेक्ट्रान हैं.
3 elements with oxidation state -2, having 6 out of 8 electrons in valence shell.
O-8, S-16 & Se-34
7) 3 तत्व जिनकी आक्सिकरण अवस्था -१ है, संयोजक कक्षा कुल ८ मे से ७ एलेक्ट्रान हैं.
3 elements with oxidation state -1, having 7 out of 8 electrons in valence shell.
F-9, Cl-17 & Br-35
8) ३ तत्व जिनकी संयोजक कक्षा भारी हुई है, जिससे वे रसायनिक प्रक्रिया मे भाग नही लेते.
3 elements which do not react as they have complete valence shell.
He-2, Ne-10 & Ar-18
9) आवर्त १ के दो तत्व.2 elements of period 1.
H-1 & He-2
10) आवर्त २ के ८ तत्व.8 elements of period 2.
Li-3, Be-4, B-5, C-6, N-7, O-8, F-9 & Ne-10
11) आवर्त ३ के ८ तत्व.8 elements of period 3.
Na – 11, Mg-12, Al-13, Si-14, P-15, S-16, Cl-17 & Ar-18
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
कोई संदेह या सवाल के लिए मैल करें (For doubts or questions) mail to: nikhilesh@asanvigyan.in
